Introduction
In today’s digital age, we rely heavily on our computers for almost every aspect of our lives, from work to entertainment. However, the rising costs of software subscriptions, coupled with the frustration of dealing with expensive and often unfixable hardware (like Apple products), has left many users searching for a better alternative.
If you're tired of paying for software that doesn't fully meet your needs, or if you're fed up with forced obsolescence that leaves your devices unusable after just a few years, it's time to consider Linux Mint. Linux Mint is a free, open-source operating system that provides a fresh alternative to Windows and MacOS. It’s user-friendly, highly customizable, and has a strong focus on privacy and security.
This blog post will take you through everything you need to know about Linux Mint—what it is, why it’s worth considering, and how to install it on your computer. Whether you're a complete beginner or someone with a bit of technical know-how, by the end of this guide, you'll have a clear understanding of why Linux Mint might be the perfect solution for you.

What is Linux Mint?
Linux Mint is a free, open-source operating system that is based on the popular Ubuntu Linux distribution. It was designed with the goal of providing a more user-friendly alternative to other Linux distributions, making it accessible even to people who have little to no experience with Linux. Since its first release in 2006, Linux Mint has grown to become one of the most popular Linux distributions in the world, particularly among users who are looking for an alternative to Windows and MacOS.
Key Features of Linux Mint
- User-Friendly Interface: Linux Mint is known for its clean, simple, and easy-to-navigate interface. It closely resembles the look and feel of traditional operating systems like Windows, which makes the transition easier for new users.
- Pre-Installed Software: Linux Mint comes with a wide range of pre-installed software, including the LibreOffice suite, Firefox web browser, and multimedia tools, so you can get started right away without needing to download additional programs.
- Customisability: One of the standout features of Linux Mint is its customisability. Users can tweak almost every aspect of the operating system, from the desktop environment to the system settings, to suit their personal preferences.
- Security and Privacy: Linux Mint places a strong emphasis on security and privacy. The OS receives regular updates, and the Linux Mint team is committed to protecting users' data and privacy.
Community Support:
Linux Mint has a vibrant and active community of users and developers who contribute to the project. This means that there is a wealth of resources available, including forums, documentation, and community-contributed software.
Update Frequency and Community Support
Linux Mint is actively maintained and regularly updated, with new versions typically released every six months. These updates include security patches, new features, and improvements to existing tools. This regular update cycle ensures that users have access to the latest software and security enhancements without the forced updates often seen in commercial operating systems.
The Linux Mint community is one of its greatest strengths. It’s a welcoming and helpful environment where users can find answers to almost any question they might have. Some of the best communities to find how-tos and advice include:
- The Linux Mint Forums: The official Linux Mint forums are a great place to start. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced user, you can find detailed guides, troubleshooting tips, and support from other Linux Mint users.
- Reddit (r/linuxmint): The Linux Mint subreddit is an active community where users share tips, ask questions, and discuss the latest developments in the Linux Mint world.
- Linux Mint Documentation: The official documentation is comprehensive and user-friendly, offering step-by-step guides on installing and using Linux Mint.
- YouTube Channels: Channels like “LearnLinuxTV” and “The Linux Experiment” offer video tutorials that can help visual learners get the most out of Linux Mint.

Why You Should Consider Switching to Linux Mint
Switching to Linux Mint can be a game-changer, especially if you're tired of the limitations, costs, and frustrations associated with commercial operating systems like Windows and MacOS. Here are several compelling reasons why Linux Mint might be the perfect fit for you.
Cost Savings: Free and Open-Source
One of the most significant advantages of Linux Mint is that it’s completely free. Unlike Windows and MacOS, which often require expensive licenses and software subscriptions, Linux Mint is an open-source project. This means you don’t have to spend a dime to download, install, and use it. Moreover, most of the software available for Linux Mint is also free, further reducing your overall computing costs.
Control Over Your Software
Linux Mint gives you full control over your operating system. Unlike commercial operating systems, which often come with bloatware, forced updates, and unwanted features, Linux Mint allows you to decide what you want to install and when you want to update. This level of control ensures that your computer remains uncluttered and runs smoothly, without unexpected interruptions or annoyances.
Flexibility and Customization
If you’ve ever wished you could tailor your operating system to better suit your needs, Linux Mint is the answer. The OS offers a wide range of customization options, from changing the desktop environment and themes to tweaking system settings and installing only the software you need. This flexibility allows you to create a computing environment that works best for you, whether you prefer a minimalist setup or a feature-rich desktop.
Security and Privacy
Security is a top priority for Linux Mint. The operating system is less prone to malware and viruses compared to Windows, making it a safer choice for users who are concerned about their digital security. Additionally, Linux Mint respects your privacy, offering features that help you maintain control over your personal data. Unlike some commercial operating systems, Linux Mint does not track your activities or sell your data to third parties.
Performance on Older Hardware
One of the standout benefits of Linux Mint is its ability to breathe new life into older computers. If you have a PC or Mac that’s been rendered obsolete by the latest updates from Windows or Apple, Linux Mint can help you extend its lifespan. The OS is lightweight and optimized to run efficiently on older hardware, meaning you can enjoy a fast and responsive system without the need for expensive upgrades.
Frequent Updates and Community Support
As mentioned earlier, Linux Mint is regularly updated with new features, security patches, and improvements. This continuous development ensures that your system remains secure, stable, and up-to-date. Additionally, the vibrant Linux Mint community is always there to help. Whether you need advice on troubleshooting an issue, tips on customization, or guidance on using new features, you’ll find plenty of support from fellow users and developers.

Potential Drawbacks of Linux Mint
While Linux Mint offers many advantages, it’s essential to consider some potential drawbacks before making the switch. Understanding these challenges can help you make an informed decision and prepare you for any adjustments you might need to make.
Learning Curve
For users who are accustomed to Windows or MacOS, transitioning to Linux Mint can come with a learning curve. The way Linux handles software installation, system updates, and file management is different from what you might be used to. While Linux Mint is designed to be user-friendly, it still requires some time to get familiar with the new environment. However, once you get the hang of it, many users find Linux Mint to be intuitive and easy to use.
Fortunately, there is a tonne of help out there to support your learning, for example, this cheat sheet by Geeks for Geeks.

Software Compatibility
One of the main challenges with switching to Linux Mint is software compatibility. Some programs and applications that are standard on Windows or MacOS may not have direct equivalents in the Linux ecosystem. For example, Adobe Creative Suite, Microsoft Office, and certain proprietary software may not run natively on Linux. While there are often open-source alternatives (like GIMP for Adobe Photoshop or LibreOffice for Microsoft Office), these alternatives may not offer the exact same features or experience.
Gaming Limitations
If you’re a gamer, you might find Linux Mint’s gaming support to be limited compared to Windows. While Linux gaming has come a long way in recent years, thanks to platforms like Steam’s Proton and Lutris, some AAA games may not run as smoothly or at all on Linux. Additionally, game developers often prioritize Windows for game releases, meaning you might have to wait longer for Linux support or rely on third-party tools to get games running.
Hardware Compatibility
Although Linux Mint is designed to work on a wide range of hardware, there can still be issues with compatibility, especially with newer or more niche hardware. Some devices, such as printers, graphics cards, or Wi-Fi adapters, may require additional drivers or might not be fully supported. However, the Linux Mint community is a great resource for finding solutions to these issues, and many manufacturers are increasingly providing better Linux support. We run a Brother MFC-J6930DW on Linux mint. Out of the box it prints fine but we did have to go to the Brother website and download the model specific drivers then install them through the Terminal to get it fully operational.
Brother Print Drivers
https://support.brother.com/g/b/downloadtop.aspx?c=au&lang=en&prod=mfcj6930dw_us_eu_as
Step 1. Download the tool.(linux-brprinter-installer-..-.gz)
The tool will be downloaded into the default "Download" directory.
(The directory location varies depending on your Linux distribution.)
e.g. /home/(LoginName)/Download
Step 2. Open a terminal window.
Step 3. Go to the directory you downloaded the file to in the last step. By using the cd command.
e.g. cd Downloads
Step 4. Enter this command to extract the downloaded file:
Command: gunzip linux-brprinter-installer-2.2.4-1.gz
e.g. gunzip linux-brprinter-installer-2.1.1-1.gz
Step 5. Get superuser authorization with the "su" command or "sudo su" command.
Step 6. Run the tool:
Command: bash linux-brprinter-installer-..- Brother machine name
e.g. bash linux-brprinter-installer-2.2.4-1 MFC-J6930DW
Step 7. The driver installation will start. Follow the installation screen directions.
When you see the message "Will you specify the DeviceURI ?",
For USB Users: Choose N(No)
For Network Users: Choose Y(Yes) and DeviceURI number.
The install process may take some time. Please wait until it is complete.
Community Support vs. Professional Support
While the Linux Mint community is vibrant and helpful, it’s important to note that support is often community-driven rather than provided by a professional helpdesk. This means that if you run into a problem, you’ll likely be searching forums, asking questions on Reddit, or reading documentation to find a solution. While the community is generally quick to help, it’s not the same as having a dedicated customer support team to call.
System Requirements and Compatibility
Before switching to Linux Mint, it's crucial to understand the system requirements and compatibility considerations. Whether you're installing Linux Mint on a brand-new computer or breathing new life into an older machine, ensuring your hardware is up to the task will make the transition smoother.
Minimum and Recommended System Requirements
Linux Mint is known for being lightweight and resource-efficient, making it suitable for a wide range of hardware, including older computers. Below are the minimum and recommended system requirements:
- Minimum System Requirements:
- 1GB RAM (2GB recommended for a more comfortable experience)
- 15GB of disk space (20GB recommended)
- 1024x768 resolution display
- A USB port or DVD drive for installation
- Recommended System Requirements:
- 2GB RAM or more
- 20GB or more of disk space
- 1366x768 resolution display or higher
- Dual-core processor (2GHz or faster)
- Internet connection (for downloading updates and additional software)
Compatibility with Older Hardware
One of Linux Mint's biggest advantages is its compatibility with older hardware. Many users turn to Linux Mint to revive older PCs and Macs that can no longer run the latest versions of Windows or macOS. Linux Mint's lightweight nature allows it to perform well on systems with limited resources, making it an excellent choice for extending the life of older computers.
If you have an older Apple Mac that has been rendered obsolete by forced obsolescence (unable to upgrade to the latest macOS), Linux Mint can be a lifesaver. By installing Linux Mint, you can continue using your Mac for years to come, with access to a modern operating system that receives regular updates and support.
Hardware Considerations
While Linux Mint is compatible with a wide range of hardware, there are some considerations to keep in mind:
- Graphics Cards: Linux Mint supports most integrated and dedicated graphics cards. However, if you're using a newer or high-end graphics card, you may need to install additional drivers for optimal performance.
- Printers and Peripherals: Most printers, scanners, and other peripherals work with Linux Mint out of the box. However, for some niche or older devices, you may need to search for Linux-compatible drivers or community-supported solutions.
- Wi-Fi Adapters: Most Wi-Fi adapters are supported, but some may require additional drivers or tweaks to work correctly. It's always a good idea to check the Linux Mint forums or hardware compatibility lists if you're unsure.
Preparing Your Hardware for Installation
Before installing Linux Mint, it's essential to prepare your hardware. This preparation includes backing up your data, ensuring your system meets the requirements, and downloading the necessary tools for installation. If you're installing Linux Mint on an older computer, you might also want to consider upgrading your RAM or replacing an old hard drive with a solid-state drive (SSD) to improve performance.

How to Install Linux Mint
Installing Linux Mint is a straightforward process, even for those who may not be particularly tech-savvy. This section will guide you through each step of the installation process, from preparing your computer to setting up Linux Mint for the first time.
Preparing for Installation
Before you begin the installation process, it’s crucial to prepare your system to ensure everything goes smoothly.
- Backup Your Data: If you’re installing Linux Mint on a computer that already has an operating system, it’s important to back up all your important files and data. While the installation process is generally safe, it’s always better to be cautious and avoid any potential data loss.
- Choose the Right Version of Linux Mint: Linux Mint comes in several different editions, with the most popular being the Cinnamon, MATE, and Xfce editions. Each edition has a different desktop environment, so choose the one that best fits your needs:
- Cinnamon: The flagship edition, offering a modern and full-featured desktop experience.
- MATE: A more traditional desktop environment, known for its speed and efficiency.
- Xfce: A lightweight edition, ideal for older hardware or users who prefer a simpler interface.
- Download the Linux Mint ISO: Visit the official Linux Mint website and download the ISO file for the edition you’ve chosen. The ISO file is a disk image that contains the entire Linux Mint operating system.
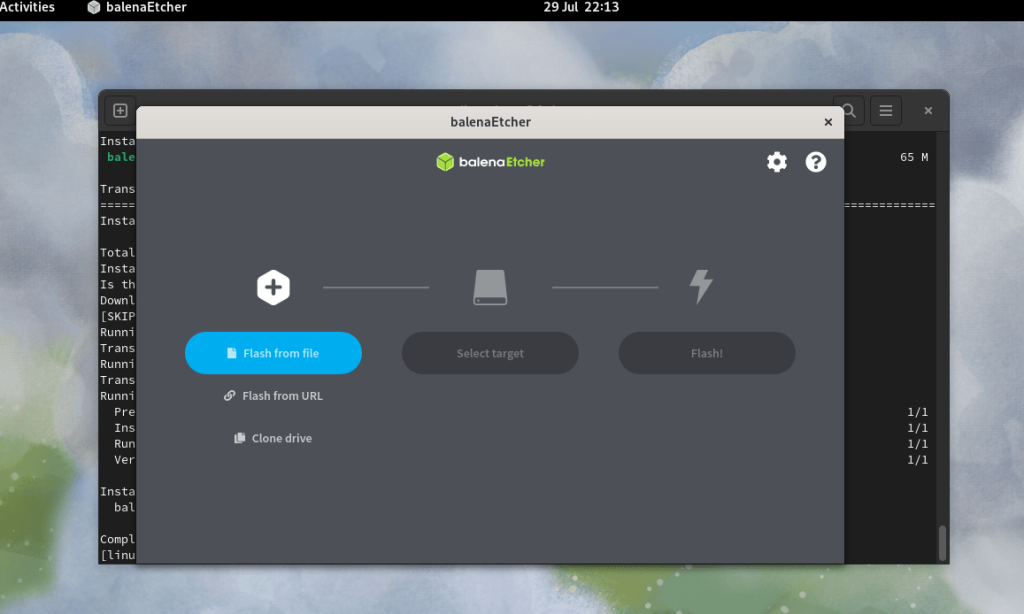
Creating a Bootable USB Disk
Once you’ve downloaded the Linux Mint ISO, the next step is to create a bootable USB disk. This will allow you to install Linux Mint on your computer.
- Tools Needed:
- A USB flash drive (at least 4GB in size)
- A computer with internet access
- Software to create the bootable USB (e.g., balenaEtcher)
- Step-by-Step Guide:
- Download and Install BalenaEtcher: BalenaEtcher is a free tool that simplifies the process of creating bootable USB disks. It’s available for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Insert Your USB Drive: Plug the USB drive into your computer. Make sure it’s empty or that you’ve backed up any important files, as the process will erase all data on the drive.
- Open BalenaEtcher: Launch BalenaEtcher and select the Linux Mint ISO file you downloaded earlier.
- Select Your USB Drive: Choose your USB drive from the list of available drives.
- Flash the Drive: Click the “Flash” button to start the process. BalenaEtcher will write the Linux Mint ISO to your USB drive, making it bootable.
- Safely Eject the USB Drive: Once the process is complete, safely eject the USB drive from your computer.
Installing Linux Mint
With your bootable USB drive ready, it’s time to install Linux Mint on your computer.
- Boot from the USB Drive:
- Insert the USB Drive: Plug the bootable USB drive into the computer where you want to install Linux Mint.
- Access the Boot Menu: Restart the computer and access the boot menu by pressing the appropriate key during startup (usually F12, F2, ESC, or DEL, depending on your computer).
- Select the USB Drive: From the boot menu, select your USB drive to boot from it.
- Guided Installation Process:
- Welcome Screen: After booting from the USB drive, you’ll see the Linux Mint welcome screen. Here, you can choose to try Linux Mint without installing it or proceed directly to installation. If you’re ready to install, click “Install Linux Mint.”
- Language and Keyboard Layout: Choose your preferred language and keyboard layout.
- Preparing to Install: The installer will check if your system meets the requirements. It’s recommended to connect to the internet during installation to download updates and third-party software (e.g., codecs for media playback).
- Installation Type: You’ll be prompted to choose the installation type. You can install Linux Mint alongside your existing operating system (dual boot), erase the entire disk and install Linux Mint, or use advanced options for custom partitioning.
- Partitioning: If you choose a custom installation, you can create, resize, or delete partitions. Otherwise, the installer will handle this automatically.
- User Setup: Set up your user account by entering your name, computer name, username, and password. You can also choose whether to log in automatically or require a password.
- Begin Installation: Once everything is set, click “Install Now” to begin the installation. The process may take some time, depending on your hardware.
- Final Steps:
- Remove the USB Drive: After installation is complete, the system will prompt you to remove the USB drive and press Enter to reboot.
- First Boot: Your computer will now boot into Linux Mint for the first time.
Post-Installation Setup
After installing Linux Mint, there are a few essential steps to get your system up and running.
- Update the System: The first thing you should do is update your system to ensure you have the latest security patches and software updates. Open the Update Manager and install all available updates.
- Install Additional Software: Depending on your needs, you might want to install additional software. The Software Manager in Linux Mint makes it easy to browse and install a wide range of applications.
- Customize the Desktop Environment: Take some time to explore and customize your desktop environment. You can change the theme, wallpaper, and layout to make your Linux Mint experience uniquely yours.
Installing and Using Wine
One of the most significant concerns for users switching from Windows to Linux is the ability to run Windows-specific software. While Linux Mint offers a wide range of native applications, there might still be certain programs that don’t have direct Linux equivalents. This is where Wine comes in—a compatibility layer that allows you to run many Windows applications on Linux.
Wine, which stands for "Wine Is Not an Emulator," is a free and open-source software that enables users to run Windows applications on Unix-like operating systems such as Linux. Unlike traditional emulation, which requires a separate operating system to run within a virtual machine, Wine translates Windows API calls into POSIX calls in real-time, allowing Windows software to run directly on Linux.
Wine is not perfect, and not every Windows application will work flawlessly. However, it does support a large number of popular applications, making it an invaluable tool for users who rely on specific Windows programs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Wine
Installing Wine on Linux Mint is straightforward and can be done using the terminal or the Software Manager. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Install Wine via Terminal:
- Open the Terminal: You can open the terminal by pressing
Ctrl + Alt + T. - Add the WineHQ Repository: To get the latest version of Wine, add the official WineHQ repository by running the following commands:
sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386
sudo mkdir -pm755 /etc/apt/keyrings
sudo wget -O /etc/apt/keyrings/winehq-archive.key https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/winehq.key
sudo wget -NP /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/ubuntu/dists/$(lsb_release -cs)/winehq-$(lsb_release -cs).sources
- Update Your Package List:
sudo apt update
- Install Wine: Install the latest stable version of Wine by running:
sudo apt install --install-recommends winehq-stable
- Verify the Installation: After the installation is complete, you can verify that Wine is installed by running:
wine --version
- This command should return the version of Wine installed on your system.
- Install Wine via Software Manager:
- Open Software Manager: You can find it in the main menu under "Administration."
- Search for Wine: Type "Wine" in the search bar and select the stable version.
- Install Wine: Click the "Install" button and follow the on-screen instructions.
Running Windows Applications with Wine
Once Wine is installed, you can start using it to run Windows applications.
- Download the Windows Application: Download the
.exefile for the Windows application you want to run. - Run the Installer with Wine: Navigate to the directory where the
.exefile is located, right-click on the file, and select "Open with Wine Windows Program Loader." This will start the installation process just like it would on a Windows PC. - Launch the Application: Once installed, you can run the application by double-clicking its icon or running it through Wine in the terminal.
Examples of Popular Windows Programs Compatible with Wine
Wine supports a wide range of Windows applications. Here are a few examples:
- Microsoft Office: Many users successfully run older versions of Microsoft Office (like Office 2010) using Wine.
- Adobe Photoshop: Certain versions of Adobe Photoshop work well with Wine, allowing you to continue using this popular software on Linux.
- Notepad++: This versatile text editor is a favorite among developers and runs smoothly under Wine.
Troubleshooting and Optimizing Wine Performance
While Wine is a powerful tool, you might encounter some issues depending on the application you’re trying to run. Here are some tips to help troubleshoot and optimize your experience:
- Check the AppDB: The Wine Application Database (AppDB) is a community-driven resource where users share their experiences running Windows software with Wine. Before installing an application, check the AppDB for compatibility ratings and any known issues.
- Install Winetricks: Winetricks is a helper script that makes it easier to install certain libraries and components required by some Windows applications. It can help resolve issues with application dependencies.
sudo apt install winetricks
Run in a Virtual Desktop: If you encounter graphical issues, try running the application in a virtual desktop by configuring Wine through winecfg and enabling the "Emulate a virtual desktop" option.
Getting the Most Out of Linux Mint
Now that you have Linux Mint installed and are familiar with how to run Windows applications using Wine, it’s time to explore how to get the most out of your new operating system. This section will cover recommended software, tips for customization, and the best resources for finding help and support.
Recommended Software and Applications
Linux Mint comes pre-installed with a wide range of essential software, but there are many additional applications you can install to enhance your experience. Here are some recommendations:
- Web Browsers:
- Firefox: The default browser on Linux Mint, known for its speed and privacy features.
- Brave: A privacy-focused browser with built-in ad-blocking and tracking protection.
- Vivaldi: A highly customizable browser for power users.
- Mullvad: Privacy focussed browser integrates well with the Mullvad VPN
- Floorp: Yep, its based on Firefox by hardened - LINK
- Office Suite:
- LibreOffice: A full-featured office suite that’s compatible with Microsoft Office formats.
- OnlyOffice: An alternative office suite with better compatibility with Microsoft Office files.
- Multimedia:
- VLC Media Player: A versatile media player that supports almost every video and audio format.
- GIMP: An advanced image editor that serves as a free alternative to Adobe Photoshop.
- Audacity: A powerful audio editor for recording and editing sound.
- Productivity Tools:
- Thunderbird: A robust email client with calendar and task management features.
- Kdenlive: A video editor that offers a wide range of features for both beginners and professionals.
- Evolution: An email and calendar application that integrates well with GNOME desktop environments.
- System Utilities:
- Timeshift: A system restore utility that allows you to create and manage system snapshots. Very handy if you bugger up a system setting then need to restore to your last safe backup.
- BleachBit: A system cleaner that helps you free up space by removing unnecessary files.
- Vorta: By Borgbase is a fantastic backup system for each PC especially when you consider they shout you 10GB free! I highly recommend this service. There are heaps of Youtube videos to help you get it up and running. The paid plans are far more affordable than Backblaze too.
Tips for Customization
One of the best aspects of Linux Mint is how customizable it is. Here are some tips to help you tailor your Linux Mint experience:
- Changing Themes: Linux Mint allows you to easily change the look and feel of your desktop. You can choose from a variety of themes for your window borders, icons, and controls. Simply go to "Themes" in the System Settings to explore and apply new themes.
- Installing Additional Desktop Environments: If you want to try a different desktop environment, you can install additional ones such as KDE Plasma or GNOME. This gives you the flexibility to choose the interface that best suits your workflow.
- Using Applets and Desklets: Applets are small applications that you can add to your panel (taskbar), such as a weather applet or a CPU monitor. Desklets are similar, but they sit on your desktop instead of the panel. You can add these from the “Applets” and “Desklets” options in the System Settings.
- Keyboard Shortcuts: Customize keyboard shortcuts to improve your productivity. For example, you can set up shortcuts for launching applications, controlling media playback, or taking screenshots. Go to “Keyboard” in the System Settings to configure these.
- Creating Custom Scripts: If you’re comfortable with the command line, you can create custom scripts to automate repetitive tasks. For example, you could create a script to back up your files or launch a specific set of applications when you start your computer.
Finding Help and Support
The Linux Mint community is incredibly supportive, and there are plenty of resources available to help you if you run into any issues or want to learn more about your system. Here are some of the best places to find help:
- Linux Mint Forums: The official forums are a great place to ask questions, share tips, and learn from other users. The community is welcoming, and you’ll often find that your questions have already been answered by others.
- Reddit (r/linuxmint): The Linux Mint subreddit is an active community where users discuss everything from installation tips to software recommendations. It’s a great place to get quick answers and participate in discussions about Linux Mint.
- Linux Mint Documentation: The official documentation is comprehensive and provides step-by-step guides on various aspects of using Linux Mint. Whether you need help with installation, customization, or troubleshooting, the documentation is a valuable resource.
- YouTube Channels: Visual learners might find YouTube tutorials helpful. Channels like “LearnLinuxTV” and “The Linux Experiment” offer detailed guides and tips on getting the most out of Linux Mint.
- Community-Written Blogs and Articles: There are many blogs and articles written by Linux enthusiasts that cover a wide range of topics, from beginner guides to advanced tutorials. These resources can be found through a simple web search and can provide you with additional insights and tips.
Conclusion
Switching to Linux Mint can open up a world of possibilities if your looking for and alternative to the costly and sometimes restrictive environments of Windows and MacOS. Linux Mint offers a user-friendly, flexible, and secure operating system that can breathe new life into older hardware, save you money, and provide you with more control over your computing experience.
Whether you're looking to escape the cycle of forced obsolescence, reduce your software costs, or simply explore something new, Linux Mint is a robust and reliable option that’s well worth considering.
Give it a try—you might just find that it’s the perfect fit for your computing needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Is Linux Mint really free?
- Yes, Linux Mint is completely free to download, install, and use. It’s open-source software, meaning it’s developed and maintained by a community of contributors.
- Can I install Linux Mint alongside Windows or MacOS?
- Yes, Linux Mint can be installed alongside your existing operating system in a dual-boot configuration, allowing you to choose which OS to use when you start your computer.
- Will my Windows software work on Linux Mint?
- Many Windows applications can run on Linux Mint using Wine, but not all software is compatible. For programs that don’t work, you may need to find a Linux alternative.
- Is Linux Mint safe from viruses?
- Linux Mint is less susceptible to viruses and malware compared to Windows, but no system is entirely immune. It’s still important to practice safe browsing and consider using antivirus software if needed.
- How often is Linux Mint updated?
- Linux Mint releases new versions approximately every six months, with regular updates to improve security, stability, and functionality.
- Can I customize Linux Mint?
- Yes, Linux Mint is highly customizable. You can change themes, desktop environments, and install a wide range of additional software to tailor the OS to your liking.
- What is the best version of Linux Mint for older computers?
- The Xfce edition of Linux Mint is the most lightweight and is recommended for older hardware, as it consumes fewer resources and runs more efficiently.
- Where can I find help if I run into problems?
- You can find help through the Linux Mint forums, the Linux Mint subreddit, official documentation, YouTube tutorials, and various community-written blogs.
Further Reading